> Oxy-fuel combustion capture
Another approach is oxyfiring (or oxy-fuel) combustion, sometimes called oxyfuel combustion. This technology is similar to that used in existing power plants, except that rather than burning the fuels in air, they are burnt in an artificially created oxygen atmosphere. Without the nitrogen which makes up about 78 per cent of the Earth’s atmosphere, this results in a flue gas with high carbon-dioxide concentrations (greater than 80 per cent by volume). The water vapour is then removed by cooling and compressing the gas stream. Changes are required to the boiler and associated flue-gas handling system to accommodate the higher flame temperatures resulting from combustion with oxygen.
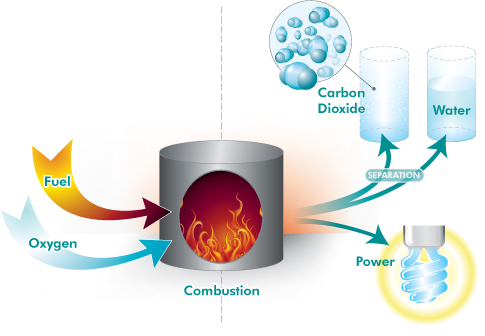
Schematic representation of CO2 capture by oxyfiring.
Source: Cooperative Research Centre for Greenhouse Gas Technologies (CO2CRC) in Australian
<< Previous page
---
Next page >>
TOP
|





