> Carbon Dioxide Capture:

CO2 can be captured from large point sources, such as large fossil fuel or biomass electricity power plants, industries with major CO2 emissions, natural gas processing, synthetic fuel plants and fossil fuel-based hydrogen production plants. The main pathways of CO2 capture are:
> pre-combustion capture
> post-combustion capture
> oxy-fuel combustion
Post-combustion capture
In post-combustion capture the CO2 is removed after fossil fuel burning. This is the method that would be applied to most conventional power plants. Here, carbon dioxide is captured (‘scrubbed') from the exhaust (or ‘flue') gases using amine scrubbers.
The technology is well understood and is currently used in other industrial applications, although not at the same scale as might be required in a commercial scale CCS power station.
Pre-combustion capture
In pre-combustion capture, the fuel is decarbonised through gasification with oxygen or through steam reforming under pressure (around 30-70atm) to produce ‘synthesis gas’, which contains CO and H2O. Syngas is then passed through catalyst beds to produce CO2 and H2. Finally, the CO2 (at 30-35%) is separated from H2 by physical or chemical solvents. CO2/H2 separation occurs at very high pressures (pressure difference up to 80bar) and high temperature (300-700°C), which makes the process more complex and costly.
Pre-combustion capture is costly but it produces a more concentrated CO2 gas stream. Pre-combustion capture is widely applied in fertilizer manufacturing and in hydrogen production.
Oxyfuel
In oxy-fuel combustion, fuel is burnt with nearly pure oxygen (up to 97%) instead of air, resulting in flue gas mixture of mainly (75% on wet basis) CO2 and water vapour. Due to the high concentration of CO2 and condensable water vapour, the CO2 separation stage is easier compared to the same stage in other two capture options and involves simple condensation of water vapour, followed by extraction of CO2. CO2 is captured by direct physical compression and cooling techniques.
CO2 Separation
Various physical and chemical methods are applied to separate CO2 from the gas mixture. Capture technologies are classified into the following broad categories:
- Chemical, physical or hybrid absorption (solvent scrubbing)
- Adsorption (physical and chemical)
- Separation (using Membranes or Cryogenically)
- Bio reactors
Technologies for Carbon Capture and Time to Commercialisation
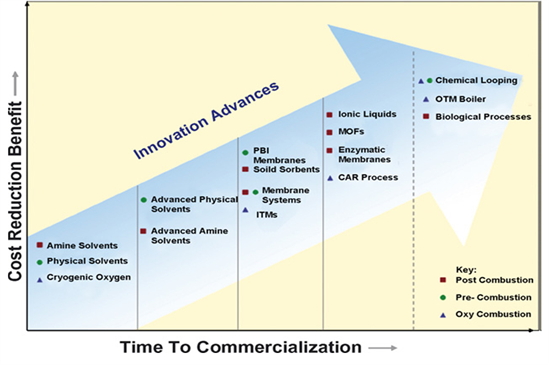
Reference: Figueroa et al 2008. Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 2;9-20.
Source: The Nottingham Centre for Carbon Capture and Storage
<< Previous page
---
Next page >>
TOP
|





